Galvanometer
Definition – The galvanometer is the device used for detecting the presence of small current and voltage or for measuring their magnitude. The galvanometer is mainly used in the bridges and potentiometer where they indicate the null deflection or zero current.
Principle of Galvanometer
The potentiometer is based on the premise that the current sustaining coil is kept between the magnetic field experiences a torque.
Construction of the Galvanometer
The construction of the potentiometer is shown in the figure below.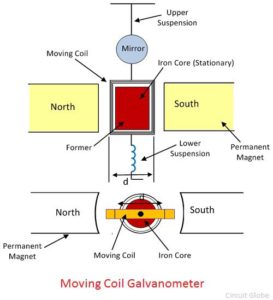
The moving coil, suspension, and permanent magnet are the main parts of the galvanometer.
Moving Coil – The moving coil is the current carrying part of the galvanometer. It is rectangular or circular and has the number of turns of fine copper wire. The coil is freely moved about its vertical axis of symmetry between the poles of a permanent magnet. The iron core provides the low reluctance flux path and hence provides the strong magnetic field for the coil to move in.
Suspension – The coil is suspended by a flat ribbon which carries the current to the coil. The other current carrying coil is the lower suspension whose torque effect is negligible. The upper suspension coil is made up of gold or copper wire which is made in the form of a ribbon. The mechanical strength of the wire is not very strong, and hence the galvanometers handle carefully without any jerks.
Mirror – The suspension carries a small mirror which casts the beam of light. The beam of light placed on the scale on which the deflection is measured.
Torsion Head – The torsion head is used for controlling the position of the coil and for adjusting the zero setting.
Applications of Galvanometer
The galvanometer has following applications. They are
It is used for detecting the direction of current flows in the circuit. It also determines the null point of the circuit. The null point means the situation in which no current flows through the circuit.
It is used for measuring the current.
The voltage between any two points of the circuit is also determined through galvanometer.
Leave a Reply